In the intricate world of electrical infrastructure, ensuring the reliability and longevity of high-voltage equipment is paramount. Unseen and often unheard, a silent threat known as Partial Discharge (PD) constantly jeopardizes the integrity of insulation systems. These localized dielectric breakdowns, though small, are precursors to catastrophic failures, leading to costly downtime, equipment damage, and potential safety hazards. This is where the Partial Discharge Detector emerges as an indispensable tool, offering a critical line of defense in preventative maintenance strategies.
What is Partial Discharge and Why Does it Matter?
Partial discharge refers to a localized electrical discharge that only partially bridges the insulation between two conductors. It occurs when there are imperfections or voids within the insulation material, leading to localized electrical stress that exceeds the dielectric strength of the void. Over time, these continuous discharges degrade the insulation, eventually leading to complete insulation breakdown and equipment failure.
The significance of detecting PD cannot be overstated. Early detection allows for timely intervention, preventing minor issues from escalating into major problems. Without effective PD detection, operators are left vulnerable to unexpected outages, reduced equipment lifespan, and increased operational costs.
How Partial Discharge Detectors Work
Partial Discharge Detectors are sophisticated instruments designed to identify and analyze these subtle electrical phenomena. They work by sensing the various physical effects produced by partial discharges, which can include:
- Electrical Pulses: The most direct method, detecting transient currents or voltages generated by PD.
- Acoustic Emissions: PD generates ultrasonic sound waves that can be picked up by acoustic sensors.
- Electromagnetic Emissions: PD emits electromagnetic waves in the radio frequency (RF) spectrum.
- Light Emissions: In some cases, PD can produce faint light, detectable by optical sensors.
Modern PD detectors often combine multiple detection methods to provide a comprehensive assessment of insulation health. They process the signals, displaying them in various formats such as phase-resolved partial discharge (PRPD) patterns, which help experts diagnose the type and severity of the discharge.
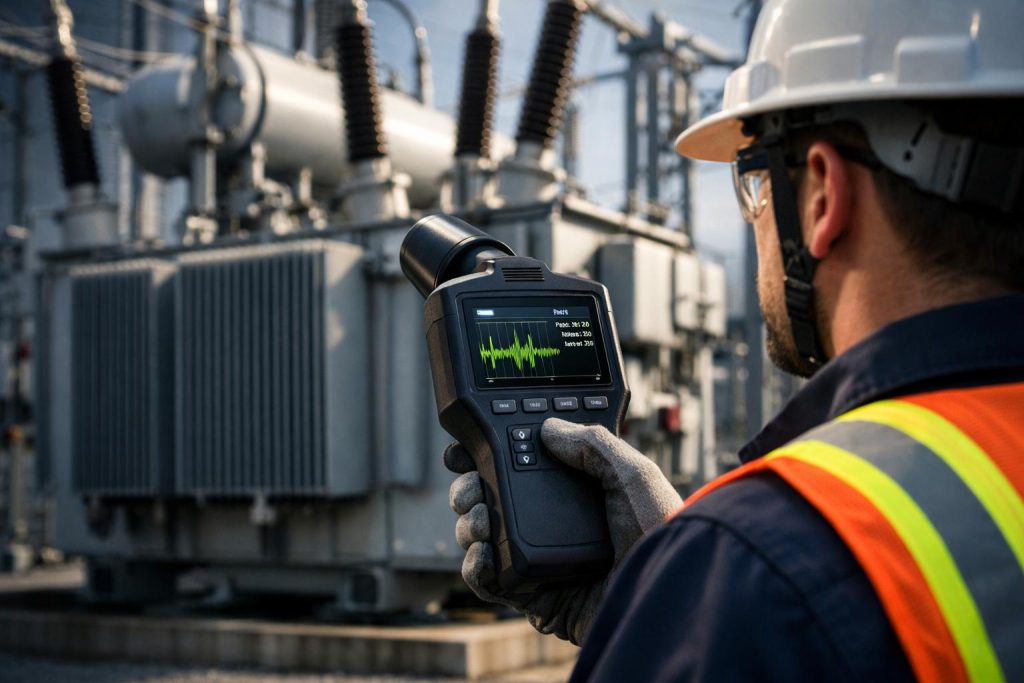

A technician utilizing a modern handheld Partial Discharge Detector to assess high-voltage equipment in a substation. The device’s screen displays real-time waveform data, crucial for on-site diagnostics.
Key Features to Look for in a High-Quality PD Detector
When selecting a Partial Discharge Detector, several features are crucial for effective and efficient operation:
- High Sensitivity: The ability to detect even the smallest discharges is vital for early warning.
- Portability and Ergonomics: Handheld and lightweight designs are essential for field use in various environments.
- Advanced Data Analysis: Features like PRPD pattern analysis, trend analysis, and reporting capabilities are critical for accurate diagnosis and predictive maintenance.
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive controls and clear displays enhance usability and reduce training time.
- Multi-Sensor Capability: The ability to integrate different types of sensors (e.g., acoustic, RF) for comprehensive data collection.
- Environmental Robustness: Designed to withstand harsh industrial conditions.
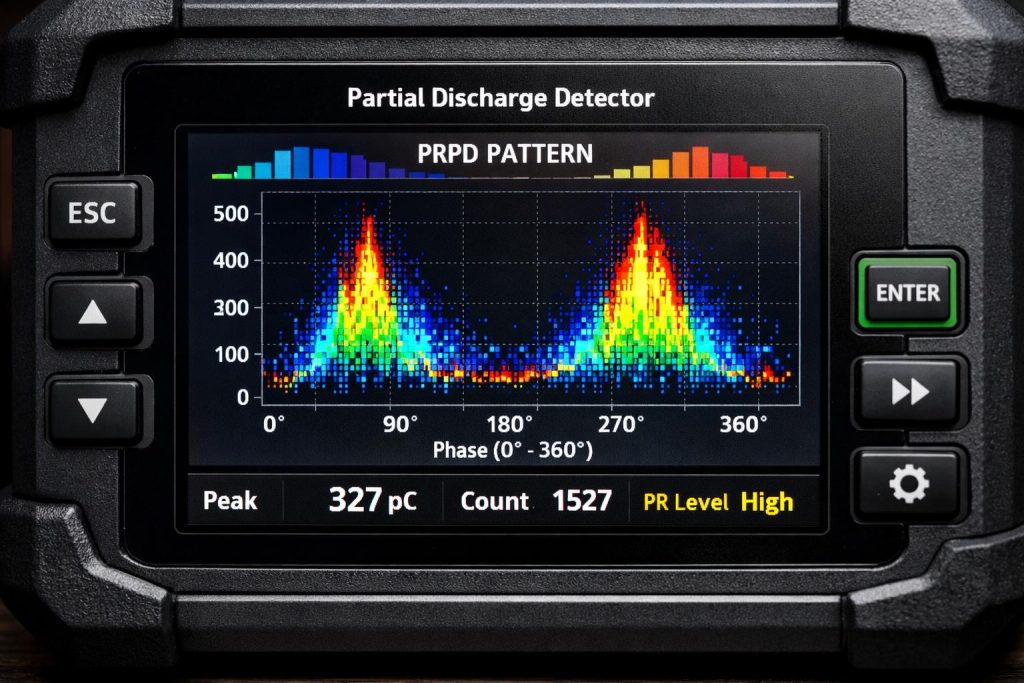
A detailed view of a Partial Discharge Detector’s digital interface, showcasing a Phase-Resolved Partial Discharge (PRPD) pattern. This visual representation is key for identifying the characteristics and potential sources of insulation degradation.
Applications Across Industries
Partial Discharge Detectors are indispensable across a wide range of industries and electrical assets, including:
- Power Generation & Transmission: Monitoring transformers, switchgear, generators, and cables in power plants and substations.
- Industrial Facilities: Ensuring the reliability of motors, switchgear, and power distribution systems in manufacturing plants.
- Renewable Energy: Assessing the health of wind turbine generators and solar farm components.
- Railways & Transportation: Inspecting traction transformers and overhead line equipment.
By regularly employing PD detection, organizations can transition from reactive maintenance to proactive, condition-based maintenance, significantly improving operational efficiency and safety.
The Undeniable Benefits of Investing in PD Detection
The integration of Partial Discharge Detectors into a maintenance program yields numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Safety: By identifying potential insulation failures before they lead to breakdowns, the risk of electrical fires, explosions, and personnel injury is drastically reduced.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: Early detection and remediation of PD allow for repairs or replacements to be made before extensive damage occurs, thereby extending the operational life of valuable assets.
- Reduced Downtime and Operational Costs: Preventative maintenance based on PD detection minimizes unplanned outages, leading to significant savings in repair costs, lost production, and emergency services.
- Optimized Maintenance Scheduling: Condition-based monitoring allows maintenance activities to be scheduled precisely when needed, avoiding unnecessary interventions and optimizing resource allocation.
- Improved System Reliability: A robust PD detection program contributes to a more stable and reliable electrical grid or industrial operation.
Conclusion
The Partial Discharge Detector is more than just a testing instrument; it is a cornerstone of modern electrical asset management. In an era where electrical reliability is non-negotiable, investing in advanced PD detection technology is a strategic decision that safeguards assets, enhances safety, and ensures continuous operation. Embrace the power of early detection to protect your critical electrical infrastructure from hidden threats and secure a more reliable future.
