In the intricate world of electrical infrastructure, ensuring the reliability and longevity of high-voltage assets is paramount. Unseen and often unheard, partial discharge (PD) poses a significant threat, gradually degrading insulation and leading to catastrophic failures if left undetected. This is where the advanced capabilities of an ultrasonic partial discharge detector become indispensable, offering a proactive approach to maintenance and asset management.
What is Partial Discharge and Why Does it Matter?
Partial discharge refers to localized dielectric breakdowns in a small portion of an electrical insulation system under high voltage stress. These discharges do not completely bridge the insulation between conductors but can cause progressive deterioration, eventually leading to complete insulation failure. The consequences can be severe, ranging from costly equipment damage and unplanned outages to safety hazards.
Traditional inspection methods often fall short in identifying these subtle yet critical precursors to failure. Ultrasonic PD detectors, however, leverage the acoustic emissions generated by partial discharges, providing a non-invasive and highly effective means of detection.
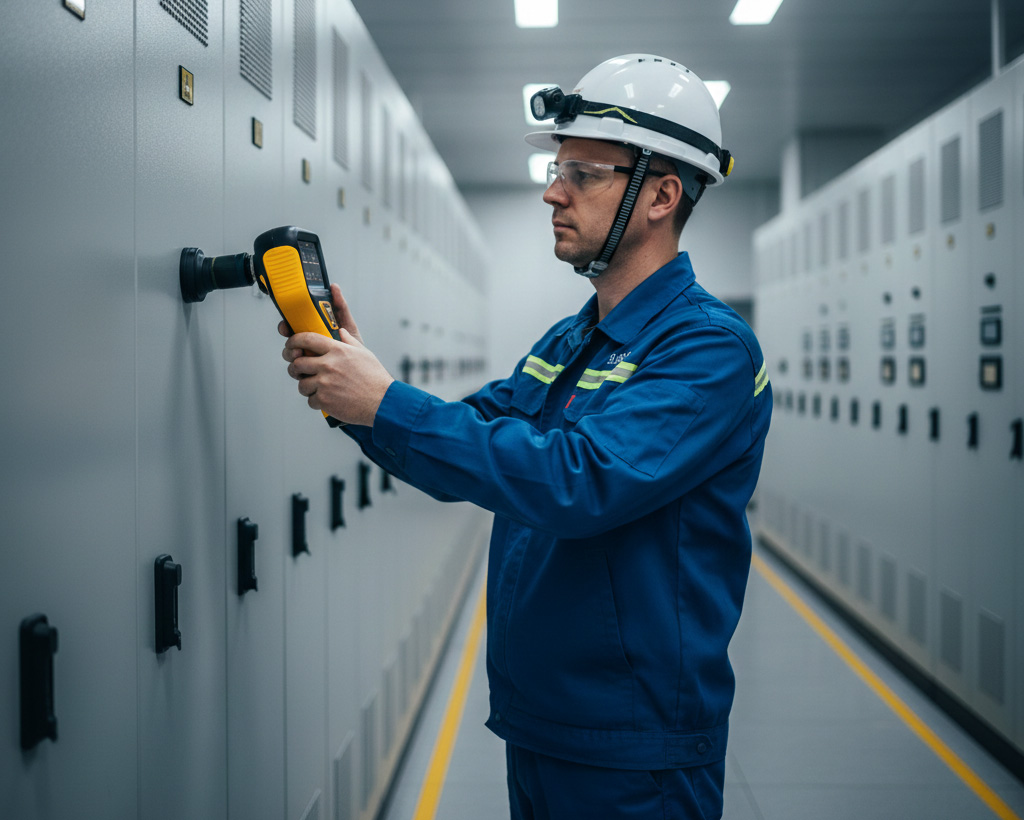

How Ultrasonic Partial Discharge Detectors Work
Partial discharges emit ultrasonic waves that are typically inaudible to the human ear. An ultrasonic partial discharge detector is designed to capture these high-frequency sound waves and convert them into an audible signal or a visual representation, allowing maintenance personnel to pinpoint the exact location and assess the severity of the discharge.
These detectors often come with various modes to provide comprehensive analysis:
Non-Contact Detection: Scanning for Anomalies from a Distance
Non-contact ultrasonic detection offers the flexibility to scan equipment from a safe distance, making it ideal for initial surveys and hard-to-reach areas. Key functionalities include:
- Amplitude Detection Mode: This mode allows for continuous or single-trigger acquisition, measuring the dB value of the PD signal, pulse count, and severity. Visual indicators (e.g., yellow, green, red) often help in quickly assessing the discharge intensity. Advanced algorithms differentiate between actual discharge and environmental interference. The ability to store sound data and convert between mV and dB provides valuable insights for analysis.
- Time Domain Graph Mode: By displaying the original waveform of the ultrasonic signal, this mode helps in understanding the characteristics of the discharge. Users can adjust trigger thresholds and sampling periods for precise data capture and mV to dB conversion.
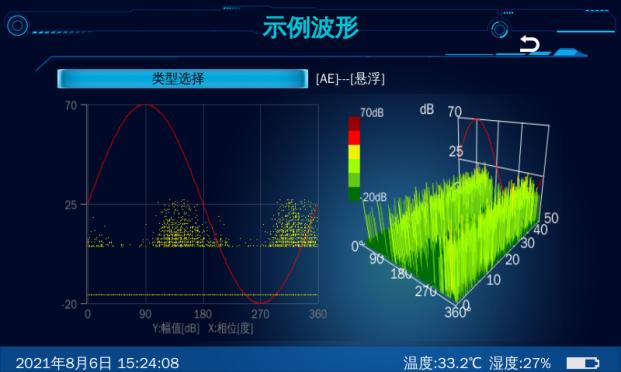
- Phase Plot Mode (PRPD/PRPS): Phase-Resolved Partial Discharge (PRPD) and Phase-Resolved Pulse Sequence (PRPS) plots are crucial for classifying different types of partial discharges and distinguishing them from noise. Modifying thresholds in this mode helps in effectively eliminating interference.
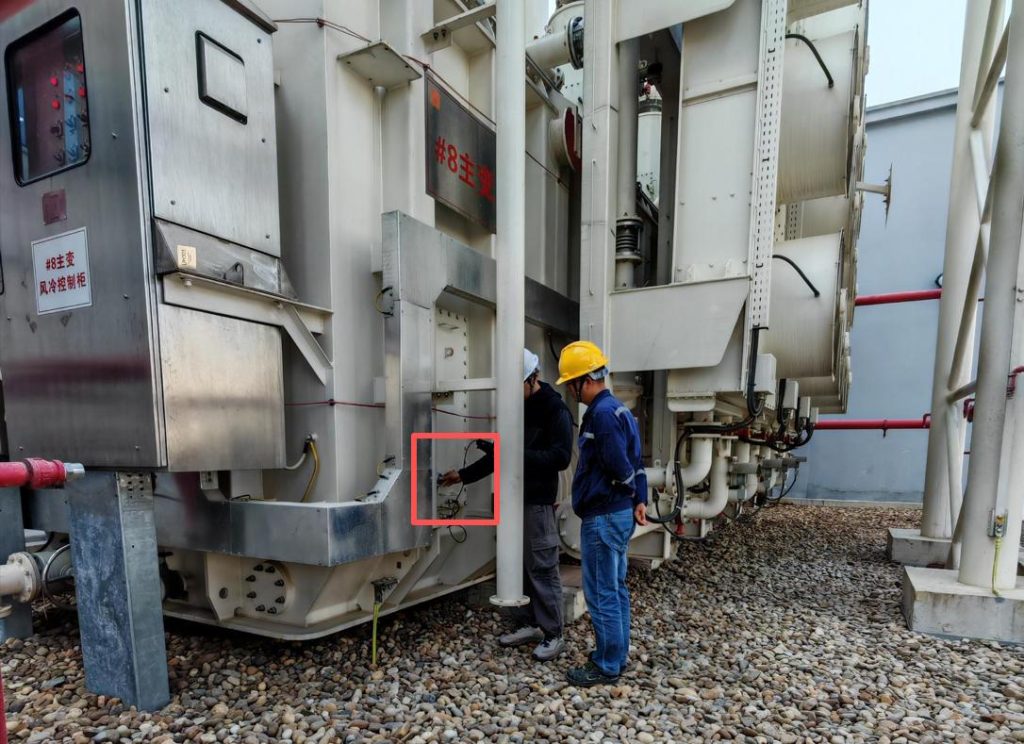
Contact Detection: Pinpointing the Source with Precision
For more detailed investigations and when direct access is feasible, contact ultrasonic detection provides enhanced sensitivity and localization. This method typically involves placing a sensor directly onto the equipment surface. In addition to the amplitude, time domain, and phase plot modes found in non-contact detection, contact detectors often feature:
- Amplitude Detection Mode (Enhanced): Provides effective value, maximum value, and frequency component information of ultrasonic signals, enabling more in-depth analysis of the discharge characteristics.
- Flight Detection Mode: This mode analyzes the relationship between the interval and amplitude of adjacent discharge pulses, offering further diagnostic capabilities. Thresholds can be set to focus on specific discharge patterns.
- Characteristic Index Detection Mode: By examining the relationship between the interval of adjacent discharge pulses and the discharge frequency, this mode helps in identifying specific types of defects and their progression.
Benefits of Integrating Ultrasonic PD Detection into Your Maintenance Strategy
Implementing ultrasonic partial discharge detectors into a predictive maintenance program offers numerous advantages:
- Early Fault Detection: Identify insulation degradation long before it leads to failure, allowing for planned interventions.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduce the risk of catastrophic failures and associated hazards to personnel.
- Cost Savings: Prevent expensive equipment damage and minimize downtime by addressing issues proactively.
- Improved Reliability: Increase the operational lifespan of electrical assets and ensure consistent performance.
- Non-Invasive Inspection: Conduct inspections without interrupting operations, maintaining productivity.

Conclusion
The ultrasonic partial discharge detector is a vital tool for modern asset management in high-voltage environments. By providing early, accurate, and non-invasive detection of insulation defects, these detectors empower maintenance teams to transition from reactive repairs to proactive, condition-based maintenance. Investing in this technology is not just about preventing failures; it’s about safeguarding assets, ensuring operational continuity, and enhancing overall safety in electrical systems.
